Health Benefits Of Cereals
The health benefits of cereals are discussed comprehensively below:
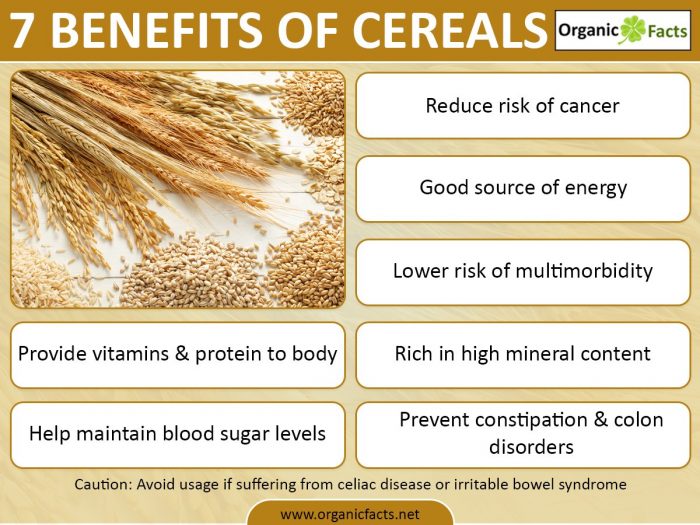
Source of Energy
Cereals are probably the greatest source of energy for humans. Providing almost 30% of total calories in a regular diet, cereals are probably the most widely consumed caloric food in America. This percentage rises in places like rural Africa and Asia where cereals are reported to supply almost 70 to 80% of energy requirements (since people in these regions cannot afford to eat other food products like fruits, vegetables, meat, or milk products). Cereals are inexpensive and a widely available source of energy; this is probably the prime reason why people from all budgets prefer cereals as the major energy provider in their diet. Cereal intake tends to be quite high amongst poor income families as they attain a good amount of energy through minimal expenditure.
High Mineral Content
In cereals, around 95% of minerals are sulfates and phosphates of magnesium, potassium, and calcium. A good amount of phosphorous, called phytin, is present in cereals. The phytates present in the cereals considerably reduce the activity of iron absorption. The unrefined cereals have more phytates as compared to refined cereals. After the seeds germinate, phytates diminish due to the breakdown of enzymes, and then the iron content is enhanced. This is the reason why malted flours of cereals are said to have more nutritional value than raw flour. Zinc, copper, and manganese are also present in small quantities. Cereals hardly have calcium and iron, but ragi is an exception to this. Amongst cereals, rice is the poorest source of iron and calcium. Ragi, millets, jowar, and bajra have high amounts of minerals and fiber.
Prevent Cancer
Whole wheat products reduce the chances of breast cancer. Cereals are rich in phytosterols or plant-based steroids and plant estrogen that stimulate the hormone estrogen. Phytosterols bind to estrogen receptors present in the tissues of the breast and block human estrogen that promotes the growth of breast cancer. Many studies have shown that colon cancers can be avoided by consuming whole wheat products or any fiber-rich cereals. Phytosterols increase the stool movement through the intestines, thereby constricting the re-absorption time of the estrogen into the blood through the colon wall.
Prevent Constipation
Cereals have both insoluble and soluble fibers like cellulose, pectin, and hemicellulose. These fibers are present in the bran and pericarp, which often gets demolished while processing, thus it is advisable to consume whole cereals to cure extreme constipation troubles. Cereals also effectively improve peristalsis in the intestine and increase the bulk of the stools, thus keeping your internal system clean. Ragi is high in cellulose and has excellent laxative properties that relieve constipation. Brown rice is also helpful for treating this disorder.
Maintain Blood Sugar Level
The fiber content in cereals decreases the speed of glucose secretion from the food, thereby maintaining sugar levels in the blood.
Provide Protein
Proteins are present in every tissue of the cereal grain. The concentrated protein-rich areas are scutellum, embryo, and the aleurone layer and moderate amounts can be found in the endosperm, pericarp, and testa. The concentration of proteins becomes denser in the endosperm from the center to the borderline. The cereal proteins are of different types; like albumins, prolamines, gliadins, globulins, and glutelins. These types of proteins are called “gluten” proteins. This gluten has extraordinary elasticity and mobile properties, mainly present in wheat grain, but also in some other types of cereal.
Cereals usually have 6-12% protein but they lack lysine. The protein content varies in each type of cereal. For instance, rice contains less protein in comparison to other cereals. In fact, the protein percentage even varies with different varieties of the same cereal. Although less in amount, the quality of rice protein is better than the protein of other cereals. When you consume cereals with pulses, the protein quality automatically improves, owing to the mutual supplementation. Pulses have high lysine content and are deficient in methionine; on the other hand, cereals have an abundance of methionine.
Multimorbidity
Recent research suggests that a greater consumption of vegetable, whole grain products, and fruits may lower the risk of multimorbidity.
Source of Vitamins
If you are suffering from a deficiency in the vitamin B complex, add whole grain cereals to your diet. Most of the vitamins of cereals are present in the outer bran, but the refining process usually reduces the vitamin B content, and thus it is advisable to consume whole grain cereals. Cereals are usually devoid of either vitamin A or vitamin C; only maize has small amounts of carotene. The cereal grains are processed to extract oils that are rich in vitamin E. Rice bran oilhas more concentrated amounts of vitamin E than other oils available on the market.
Cereal grains are rich in enzymes, particularly protease, amylase, lipases, and oxidoreductases. After the seed germinates, the amylase content actively increases. The germ encloses the protease enzymes.
Cereals are undoubtedly full of nutrition, but unfortunately, the refining process degrades their quality. The degree of milling, polishing, and refining to some extent decides the nutrient content of cereals. Some nutrients are lost during food preparation, especially vigorous washing, soaking, and cooking methods, which result in the depletion of the nutrients on the skin of the grains.
Side Effects Of Cereal Consumption
There are some disadvantages of cereals when it comes to excessive consumption. Most of the commercial varieties of cereals have an abundance of salt, sugar, and fat which should be avoided in excess. Moreover, the high-bran products often lead to discomforts like abdominal pain, bloating, and intestinal gas flatulence. If you have too much of these products, the body’s capability of iron, zinc or other mineral absorption decreases radically.
Most grains are acidic in nature, thus they can produce an acidic state within the tissues and blood. Uncontrolled cereal consumption can lead to premature aging and increases the chances of certain diseases like arthritis. Grains are comparatively more difficult to digest than salads, fruits, sprouts or vegetables, so it is always recommended to have cereals in moderate amounts to avoid chronic disease conditions. Even then, cereal grains are advised to be consumed after mild cooking. Excessive heat destroys the minerals, enzyme, and vitamins of cereals, so baking or steam cooking is preferred in most cases.
If you are suffering from coeliac disease or irritable bowel syndrome, try to avoid whole grain cereal as they aggravate such conditions.
Cereals For Children
It is often found that children are fond of cereals, as you can make them in a plethora of ways and they keep children filled for a long time. Grains have proven to be a great food for kids since ancient times; they provide energy and enough nutrition required for healthy growth. If you can feed your child with at least one cup of cereal, your child gains almost half the daily requirements of most vitamins and minerals. If you add milk or yogurt to the cereal, it will enhance the nutritional content of the meal even further. However, choosing the right cereal for your child is very important. Check out cereal grains that have ample amounts of protein, iron, and fiber. Protein aids in growth during the developmental years, iron is very important for healthy blood formation and fiber is necessary for a clean digestive tract. Good choices for your child during mealtime include millet, barley, buckwheat, rye, oats, and whole wheat.
You can also introduce juicy cereals to your kids. As said before, when you add milk to cereals they create a complete protein meal. If your child needs calories and protein, primarily go for a milk and cereal combination. On the other hand, if your child is in need of proper iron absorption, then a juice and cereal mixture will also serve beneficial.